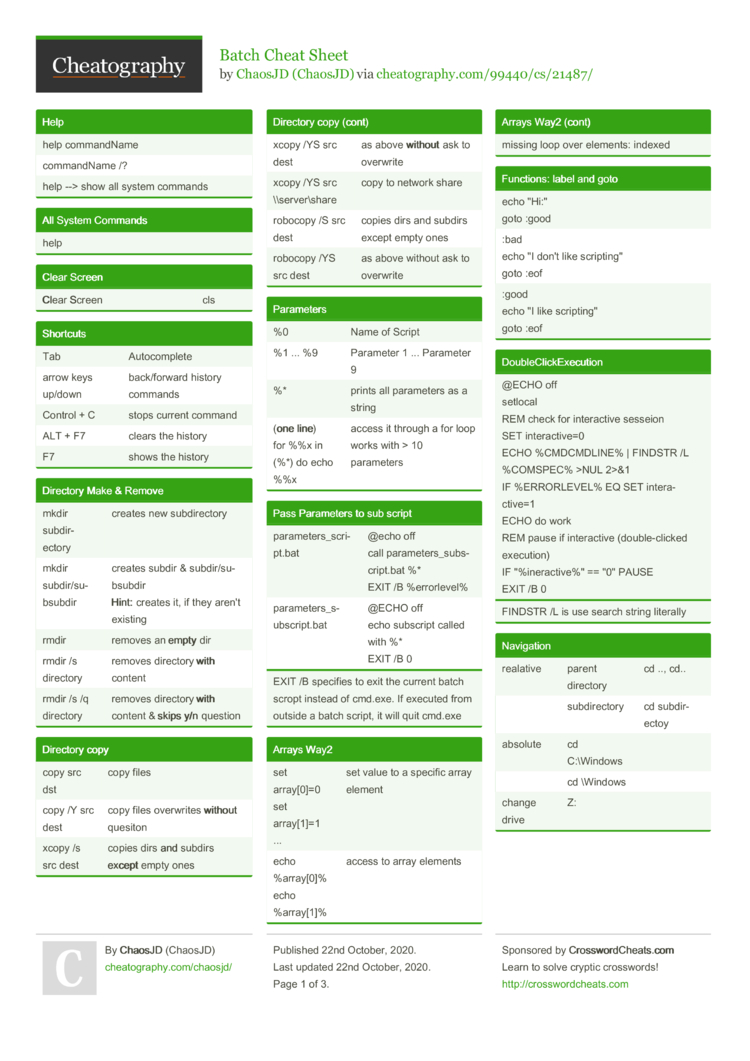
Recently, I had some tasks at work that required me to write a lot of batch files.
Here are some things about batch files that I either learned or re-discovered in the process:
Don’t use blanks when assigning values to variables
This works:
Commands marked. are Internal commands only available within the CMD shell. All other commands (not marked with.) are external commands. External commands may be used under the CMD shell, PowerShell, or directly from START-RUN. See also: A categorized list of Windows CMD commands. Microsoft Help pages: Windows Commands 8.1-10 / Windows Server 2012-2019. DOS Cheat Sheet - This Docstoc.com reference lists and explains batch file commands, command syntax, NTFS and more. MS-DOS - This Word document explains important concepts for running MS-DOS. DOS to FreeBSD Cheat Sheet - This cheat sheet offers a list of commands available on Microsoft's DOS and Windows platforms and the equivalent command. To create the batch file, open your favorite text editor. For most Windows 10 users that will likely be Notepad. Type 'notepad' into the Windows 10 desktop search box and select the appropriate.

This does not work(no error message - %foo% is just empty afterwards):
This one took me some time to figure out. I’m used to Visual Studio and the Access VBA editor, which both automatically insert these blanks into my code if I don’t do it myself. So when I wrote batch files with a simple text editor, I inserted these blanks too, without thinking.
Execute .exe and save the output to a variable
This line saves the output of foo.exe to a variable named %bar%:
(Credits for this go to user “lesmana” at Stack Overflow)
Disclaimer: I don’t try to understand it, I just copy/paste it every time I need it.
(The whole usage of the for command looks equally complicated - to see it in all its beauty, type for /? and read the help.)
Get the path and file name of the currently running batch file
There are other commands to get more file information, but to me the most important ones are these:
%~dp0outputs the path of the current batch file%~nx0outputs the name of the current batch file
To see it in action, put this into a batch file:
When the batch file is c:test.bat, it will output this:
The number zero at the end of %~dp0 and %~nx0 refers to %0, which is the currently executing batch file.
Likewise, if you pass a file as parameter %1, you can get the name of that file by using %~nx1 instead of %~nx0.
%~dp0 and %~nx0 are actually combined commands (you can also use %~n0 to get just the file name without extension, and %~x0 to get just the extension)
To see the complete list of commands, open the command line and type in call /?.
Temporarily add a folder to the %PATH% variable
When you need to refer files from a certain folder in a batch file several times and you don’t want to copy/paste the complete path every time, you can just add the folder to the %PATH% variable.
When you don’t want to (or aren’t allowed to) do this permanently on the machine, you can set the %PATH% variable in the batch file, which lasts only for the execution time of the batch file.
The following line appendsc:foo to the existing content of the %PATH% variable:
Afterwards, the %PATH% variable contains everything it contained before plusc:foo, which is probably what you want.
A second (but inferior) way would be:
This is probably not what you want, because it replaces the whole content of the %PATH% variable by c:foo !
In other words, %PATH% will only contain c:foo afterwards.
Beware: you won’t notice the difference as long as you only need files from c:foo.
But as soon as you need some other command-line tool like git or hg(or some Windows helper like regsvr32.exe), your batch file won’t find them anymore because you just deleted their locations from the %PATH%.
Variables are global in nested batch file calls
Take a look at these two batch files:
batch1.bat:
batch2.bat:
The first batch file calls the second one, so variables with the same name are shared between the two.
This means that the last line in the first batch file (echo %var%) will output bar and not foo !
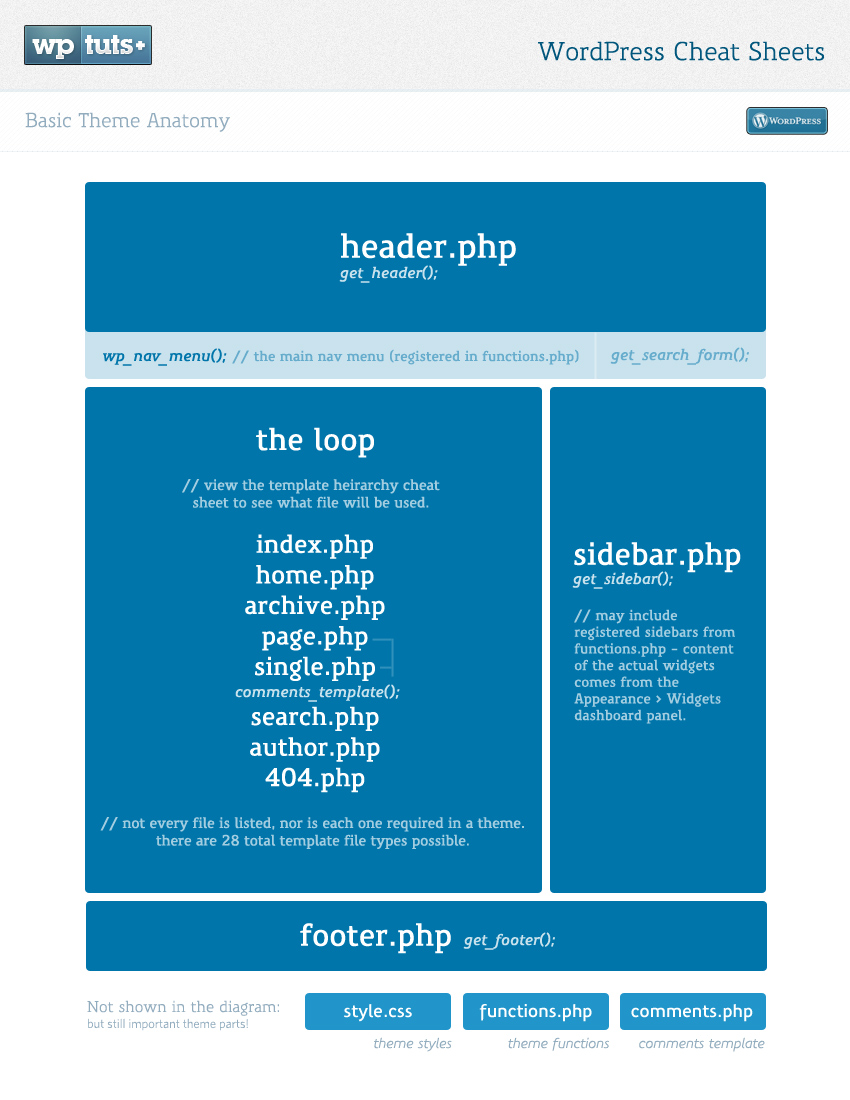
In this tutorial, you will learn about batch file commands and how they are used in batch file scripting or programming.
As discussed in the previous tutorial, a batch file is an unformatted text file or script file which contains multiple batch file commands or instructions to achieve a certain task. It has extension of .bat or .cmd.
Click here to go through the introduction of the batch file before learning batch file commands.
Batch file commands: Windows/DOS
For the ease of learning, we have listed all the batch file commands with relevant examples and explanations below. Please click on the commands to know the details.
| ASSOC | ATTRIB | CD | CHKDSK | CHOICE |
| CLS | CMD | COMP | CONVERT | COPY |
| DATE | DEL | DIR | DISKPART | DRIVERQUERY |
| ECHO | EXIT | EXPAND | FC | FIND |
| FORMAT | HELP | IPCONFIG | LABEL | MD |
| MORE | MOVE | NET | PAUSE | PING |
| RD | REM | REN | SET | SHUTDOWN |
| SORT | START | SYSTEMINFO | TASKKILL | TASKLIST |
| TIME | TITLE | TREE | TYPE | VER |
| VOL | XCOPY |
Note: Batch file commands are not case sensitive
ASSOC
The batch command ASSOC associates a file extension with a file type, or list all associations.
Example
Output
As shown in above output, it displays the file association for .txt extension.
If only ASSOC is written and executed, it will display all the file associations for every extension, instead of just .txt extension.
ATTRIB
The batch command ATTRIB is used to display the file attributes or set an attribute to a file in the working directory.
Example
Now let us suppose we have a file note.txt in our working directory. We will display its file attributes and then make it hidden and read only by adding 'ah' and 'r' attributes to it. And finally, we will remove some attributes we added as well.
Output
Here in this output, A means Archived, R means Read only and AH means Hidden file.
CD
The batch command CD helps in navigating through different directories and changing directories or displaying current directory.
Example
Output
CHKDSK
The batch command CHKDSK is used for checking error in the disk.
Example
CHOICE
The batch command CHOICE provides a list of options to the user.
Example
Output
Now that script will produce following output.
Now the console waits for your input and once you enter your answer it will terminate.
CLS
The batch command CLS clears the screen.
Example
This command just clears all the logs in command prompt screen.
CMD
The batch command CMD invokes a new command prompt window.
Example
COMP
The batch command COMP compares the size of two files and checks if they are different in size.
Example
CONVERT
The batch command CONVERTS the volumes or drives from one format to another i.e from FAT to NTFS.
Example
COPY

The batch command COPY is used for copying files from one location to another.
Batch File Cheat Sheet Pdf
Example
DATE
The batch command DATE displays the current date in the system.
Example
Output
This command DATE displays system date in command prompt as shown above.
DEL
The batch command DEL is used for deleting files.
Example
Note: DEL command only deletes files, not directories.
DIR
The batch command DIR lists all the contents of directories.
Example
DISKPART
The batch command DISKPART shows the properties of a disk partition.
Example
This script will ask for users permission to check the properties of disk partition and if allowed, will display following output in the console depending on disk properties.
DRIVERQUERY
The batch command DRIVERQUERY displays all the drivers installed and their properties.
Example
Output
This output shows the fraction of drivers list with their properties and installed date. DRIVERQUERY command shows all the drivers list, which is huge.
ECHO
The batch command ECHO is used for echoing commands on/off and printing message to the console.
Example
Output
This command ECHO displays Hello in the console as shown above.
Besides printing message, echo is also used for deciding whether or not to display the command itself. Like in this example as well, in the first line we have turned OFF echo, which makes sure that commands themselves are not printed.
If that echo wasn’t turned off, then the output would have been like:
EXIT
The batch command EXIT terminates and exits the console.
Example
In this example, as soon as HI is printed in the console, EXIT command will terminate the program and close the output console.
EXPAND
The batch command EXPAND extracts the contents of .cab file.
Example
This script will extract all the contents of xyz.cab file to the same location where xyz.cab is located.
FC
The batch command FC finds the difference between the two files and displays them to console.
Example
This script will find the difference in the content of both files and list out all of them.
FIND
The batch command FIND search the given file to find the desired string and if located, it displays the corresponding line in which the string exists.
Example
This script will search for the string “find me” in example.txt file and if it exists in example.txt, it will display the corresponding line on the console.
FORMAT
The batch command FORMAT is used for formatting a drive of format FAT 16/32 or NTFS in Windows.
Example
This script will format E drive and overwrite previous contents.
HELP
This might be the one of the most important batch file commands because with this HELP command we can know about all the other commands used in batch file or command prompt.
Example
Now this will display all the available commands with their functionalities in the console.
Since the list of commands is so much more, we have sliced the list and shown few here.
Batch File Cheat Sheet Download
Now that we have a list of batch file commands, we can also view details of their syntax and functionalities in following way:
Now this will display details of the copy command.
As you can see, it HELP COPY displays all the details about COPY command.
IPCONFIG
The batch command IPCONFIG displays Windows IP configuration.

Example
This script will generate following output.
P.S: We have hidden iPV6 address in above output.
LABEL
The batch command LABEL displays the label of a drive or volume and is also is used for adding, setting or removing a disk label.
Example
Now this will display the label of your working directory and you can set, remove or add another label.
For example, my working directory is D: and has label ‘apps’. So, it will generate following output:
MD
The batch command MD creates a new directory or folder in the working directory.
Example
This program will create a new directory abc in current working location.
MORE
The batch command MORE displays the content of a file one by one.
Example
This program will display the contents of example.txt line by line, one at a time.
MOVE
This batch command moves files from one directory to another, rename the directories and move the directories as well.
Example
In this way, MOVE command can be used to move files, directories and rename directories.
NET
The batch command NET is used for many network functionalities depending upon the commands used.
Example
To display the users:
This will generate following output:
Like users, there are many other commands:
- net accounts
- net computer
- net config
- net continue
- net file
- net group
- net help
- net name
- net pause
- net print
- net send
- net session
- net share
- net start
- net statistics
- net stop
- net time
- net use
- net view
PATH
The batch command PATH displays the path variable or it can be used to set path variable.
Example
This program will display the path of the current working directory.
PAUSE
The batch command PAUSE is used for holding the output screen till user enters a variable or a value.
Example
This program will print hi in the console and show the message ‘Press any key to continue..’ and wait for the input from the user.
PING
The batch command PING is used for sending ICMP/IP packets to the designated address over the network.
Example
Output
This script will send packets to address 127.0.1.1 and output will be displayed as follows:
RD
The batch command RD is used for removing the empty directories, directories with contents or files inside cannot be removed with RD command.
Example
REM
The batch command REM signifies comments in the batch script.
Example
Anything written after REM is interpreted as a comment and is not executed in batch programs.
REN
The batch command REN is used for renaming files and directories.
Example
SET
The batch command SET displays the list of environment variables of the system.
Example
SHUTDOWN
The batch command SHUTDOWN when invoked, shuts down the computer.
Example
SORT
The batch command SORT is used to sort the content of the file alphabetically.
Example
This script will sort the content of example.txt alphabetically either in ascending or descending order.
START
The batch command START is used to open a file or start a new program.
Example
This program will start the application paint if it is in the working location, else you will have to explicitly indicate the path of that program as well.
SYSTEMINFO
The batch command SYSTEMINFO displays all the configuration of the computer and operating system.
Example
This will generate following output depending upon the computer:
Of course, the details will be much more than this, but please try and look on your PC.
TASKKILL
The batch command TASKKILL is used to terminate a running task
Example
If you were to terminate the notepad running in your PC, then following script is used.
TASKLIST
The batch command TASKLIST lists all the running tasks in the console.
Example
TIME
The batch command TIME is used to display or set the system time.
Example
Output
The current time is displayed in the console.
TITLE
The batch command TITLE sets new title for output console.
Example
This script will set the title of output console to ‘New Console’. Thus the output console will look like:
TREE
The batch command TREE displays the tree diagram of the subdirectories to the last level.
Example
I have a folder movies. SO, if I were to run TREE in that movie folder, it will create a tree of movies inside that folder and also the subdirectories where there is movie file and subtitle file.
Output
This script will generate following output.
TYPE
The batch command TYPE is used for displaying the content of a file to an output console.
Example
This program will display all the contents of notes.txt to the console.
VER
The batch command VER displays the version of Windows or MS-DOS.
Example
Output
VOL
The batch command VOL displays the current volume label of Windows.
Example
Output
XCOPY
The batch command XCOPY is similar to COPY command but COPY command copies single file whereas XCOPY command copies entire directories including subdirectories.
Example
This script will copy test.txt from D drive to E drive.
So, these are the batch file commands along with examples.
We hope you find these batch file commands easy to learn. We will discuss more advanced concepts in next tutorials.
